The newest Russian anti-aircraft missile system(ZRS) The S-400 Triumph has received permission to export, and negotiations with foreign customers have already begun. Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Federation Dmitry Rogozin and American actor Steven Seagal announced this during the Defense Expo 2014 exhibition, which was visited the day before by Deputy general director air defense concern "Almaz-Antey" Vyacheslav Dzirkaln.
“The system has received an export passport. We are now negotiating the sale of this complex abroad. We have come quite far,” ITAR-TASS quotes Dzirklan. He suggested that a very effective and expensive air defense system is unlikely to be distributed throughout the world.
“Only countries with developed economies and good financial capabilities can afford to purchase such systems,” said the deputy head of the concern, without voicing the cost of Triumph. In 2010, the media reported that the average price of one S-400 complex could exceed $200 million.
"We are now leading marketing activities according to the S-400 air defense system. Yes, the S-300 is an effective complex, but if we already have new developments, why not offer them to our customers and potential partners,” Dzirklan said, noting that “we need to help friends and allies ensure their defense capabilities.”
The S-400 Triumph is a long- and medium-range system that is capable of simultaneously guiding up to 72 missiles at 36 targets at a distance of up to 400 kilometers. The air defense system, designed, in particular, to destroy cruise missiles, tactical and strategic aircraft (including stealth aircraft), as well as ballistic missile warheads, was adopted by government decree of April 28, 2007. The system is capable of detecting a target at a distance of up to 600 kilometers. An important difference between the S-400 and the S-300 are new anti-aircraft missiles with active homing warheads and an increased firing range.
PS According to us, there is nothing sensational in this message. Back in 2009, after two years of trial operation, there were proposals for export deliveries of the S400, the position of the developer of the S400 and subsequent projects Almaz Antey
can be considered critical, most of the leading specialists were fired and employees of the Altair Research Institute were introduced into the company, also in an abbreviated version, the company is catastrophically short of funds for normal operation and therefore the decision to sell the C 400 for export can be considered reasonable, so that At least somehow save the development team.
By the way, other enterprises in the industry are in the same situation or worse.
Everything that is happening with the ALMAZ-ANTEY company only confirms the idea that no one in Russia is going to a global confrontation with the EU countries and the USA, there are no means and opportunities for this.
And obviously, without government funding, such industries are doomed to degradation. Well, they will sell a couple of complexes - this will not solve the problems, and competitors may intercept orders.
"Grumpy" for export
Why Türkiye will not get access to S-400 systems
Turkey will not have access to internal systems S-400: Gazeta.ru found that electronic codes from the Triumph anti-aircraft missile system will remain with Moscow. Only Russian specialists will be able to repair equipment and carry out scheduled maintenance. More about, incl.
Why is this needed and how does the export S-400 differ from the original model? Alexey Sokolov.
The S-400 Triumph systems, which foreign militaries call “Grunts,” are highly coveted abroad. The characteristics are captivating - the early warning radar sees aircraft and ballistic missiles 600 km away, and after the 400 mark you can fire to kill. Experts say that the air defense systems have no analogues yet and are definitely superior to the American Patriot systems that were previously in Turkey. During the presidency of Barack Obama, the States took their air defense systems out of the country for maintenance; the Patriots never returned.
| Audio version |
The functionality of S-400s exported to Turkey is already limited, he says editor-in-chief magazine "Arms Export" Andrey Frolov.
“I think this issue has already been discussed on the Turkish side - although there were reports that they are going to produce it themselves, this production will probably concern hardware, not software. And, accordingly, in the case of hour X there is indeed an opportunity to make this complex unprepared for combat use- we lose little, because the system that will be supplied exists in export form, with roughened characteristics. Reduced number of tracked targets, noise immunity, range radar operation, rockets. All other systems that we exported were worse than what was supplied to the Russian army.”
Earlier, Western media claimed that Turkey would refuse to purchase the S-400 due to possible difficulties in the interaction of the complexes with NATO radars. But back in March, Russian Presidential Assistant for Military-Technical Cooperation Vladimir Kozhin stated that Moscow sees no obstacles to the possible supply of air defense systems to Turkey due to its membership in NATO. Mr. Kozhin emphasized: the supply agreement is very strictly regulated, and each party assumes obligations about what it has the right to do with the supplied weapons and what not.
Turkey's membership in NATO is one of the main reasons why the country will not receive full access to the systems, says Sergei Denisentsev, an expert at the Center for Analysis, Strategies and Technologies:
“You need to understand that the “friend or foe” system used in Russia differs from that used in NATO countries. The need to exclude the copying of signals from the transponder of the “friend or foe” system is very important in order to exclude the possibility of the enemy using this system in the event of some kind of conflict.”
Previously, Türkiye planned to buy an air defense system from China for $4 billion, but the deal did not take place at NATO’s request. The amount that Ankara will pay for the Triumphs was not stated, but, according to Kommersant, the possible value of the contract with Russia is more than $2 billion for four S-400 divisions.
Deliveries of the S-400 to Turkey should begin within two years.
Back in September 2014, the Chinese authorities signed a contract with the Russian Federation for the purchase of 4 divisions of S-400 Triumph anti-aircraft missile systems (ZRS), Rosoboronexport CEO Anatoly Isaikin told reporters about this in mid-April 2015. However, he did not disclose the details of the contract, noting only that China really became the first buyer of this newest domestic system Air defense. According to Isaikin, the conclusion of this contract should emphasize the strategic level of relations between Russia and China.
Anatoly Isaikin emphasized that today many countries would like to buy the S-400. However Russian industry represented by VKO Almaz-Antey, primarily works with orders from the Russian Ministry of Defense, the complexes are actively entering service with the Russian army. According to the head of Rosoboronexport, even taking into account the expansion of existing production capacities, it will be difficult to transfer the S-400 Triumph to several states at once. In this regard, China became the first sign, he emphasized.
The amount that Beijing will pay for the supply of 4 S-400 divisions has not been disclosed. But now we can confidently assume that we are talking about at least two billion dollars. According to estimates by the American portal Strategy Page, one division of Triumphs in the foreign market will cost buyers $500 million. This is provided that each delivery kit includes 8 launchers, a command vehicle, radar station and launch-charging installations.
It is worth noting that China has quite significantly reduced military exports of arms from Russia in recent years; they have learned to do a lot on their own. But in the field of air defense systems, the Chinese continued to rely on military equipment Russian production. The last major contract with China for the supply of air defense systems was completed in 2010, when the transfer to China of 15 divisions of the S-300 PMU-2 air defense system, as well as four 83M6E2 control systems, was completed. The air defense systems transferred to China were included in the air defense systems of Beijing, Shanghai and some other cities of the Middle Kingdom.
At the same time, China wanted to purchase the S-400 Triumph when this complex was just put on production line in Russia. Negotiations with Rosoboronexport began back in 2012. Moreover, judging by the information available in the public domain, the talk was initially about supplying 6 S-400 divisions to China. But even then, supply negotiations were very difficult. Firstly, the Chinese were not happy that Russia was not ready to begin supplying the systems before 2020. The first priority was to equip the Russian army with new air defense systems and even hastily opened factories in St. Petersburg, Nizhny Novgorod and Kirov, it seems, was not allowed to start deliveries to China earlier. Secondly, in Moscow there was a justified and long-standing fear that Chinese partners the latest S-400 air defense system is needed not so much for the urgent strengthening of the defense of one’s own airspace, but for a banal engineering design study and subsequent copying of the Russian one. In order to then pass off the resulting copy as a product of the Chinese military-industrial complex and begin dumping trade in the international arena. It is worth noting that China has done this many times.
Problems with possible copying of the S-400 by China
According to arms and military spending expert Stockholm international institute According to Simon Wezemann's peace research, the Russian authorities are aware of the fact that Beijing is likely to copy the technologies used in the S-400. This has already happened before with the S-300 air defense system, as well as other types of military equipment from Russia, which were supplied to China over the past two decades, the expert noted. “It is believed that the issue of copying technology was one of the most difficult when concluding agreements between the two countries. However, for Russia today this is of less importance than the political and economic benefits from the deal to sell the S-400 to Beijing,” notes Simon Wezeman.

At one time, the first modern air defense system in service with the Chinese army was the Russian S-300, which Russia began exporting in the mid-1990s. Using the technologies of the Russian complex, China subsequently created its own long-range air defense system, designated HQ-9 “Red Flag”. “At that moment, it seemed that Beijing had enough strength to create more advanced air defense systems based on the acquired technologies. However, interest in acquiring the S-400 signals that China is not yet able to do this and, at least in the short term, will be dependent on foreign technologies, in this case Russian,” Wezeman notes.
It is worth noting that in recent decades, the PRC has presented Russia with many examples of copying weapons. For example, the new Chinese BMP ZBD04 is very similar to the Russian BMP-3. The Chinese MLRS PHL-03 is exactly reminiscent of the Russian MLRS Smerch. And the J-11 fighter cannot even be distinguished externally from the domestic Su-27SK. The same can be said about the J-15 carrier-based fighter, which is very much reminiscent of our Su-33. The list goes on and on. What such copying can lead to was shown in 2013, when Russia lost the tender for the supply of 12 divisions of long-range air defense systems announced by the Secretariat defense industry Turkey. The total amount of the transaction was $4 billion. An amount that is significant for any state in the world. For this reason, the United States submitted its Patriot PAC-3 to the competition, Russia its S-300, the Europeans its SAMP/T Aster 30, and China its HQ-9. The latter, which, in fact, is an unlicensed copy of the Russian S-300PMU-1, was able to win the Turkish competition, although it is inferior in characteristics to its Russian counterpart. The most said his word low price, this became a decisive factor for Ankara. In addition, the PRC proposed to localize 10% of the production of the complexes in Turkey itself, and a large arms contract sailed to Beijing.
It is clear that with the S-400 Triumph air defense system, which so far has no analogues in the world, Russia justifiably pins special hopes on international market Long range air defense system. Even after 2020, when new system Air defense will be saturated with Russian units, and production capacity will be released for production for export. At that moment, it would be very sad to learn that on this virtual counter there would also be something similar offered by China. As practice has shown, fighting Chinese piracy in the legal field is apparently useless.

At the very least, all previous attempts by Russia to call on the Chinese to at least some kind of order were unsuccessful. The thing is that the eastern trick on the part of Chinese engineers is that when copying, they necessarily add some of their own modifications and improvements to the original product. After this, referring to the revision carried out, they declare the copy their “know-how”. Why did Moscow, understanding this perfectly well, still decide to make a deal? There can be two answers to this question. The first of them lies on the surface. Russia, which currently lives under a harsh regime of international sanctions, needs an influx of foreign currency. In the current crisis, it is not appropriate to throw away two billion dollars. But this reason is still not the main one. The main thing, according to Sergei Ishchenko from Free Press, is not finance, but politics.
At one time, the deal with the Mistrals apparently became political. The then French President Nicolas Sarkozy advocated a conciliatory position in Russia's short-lived armed conflict with Georgia in August 2008. At that moment, Sarkazy helped Moscow get out of the situation with the least reputational, financial and political losses for it. In turn, Russia could help the French president by loading the French military-industrial complex with a substantial order. At least, this version of the development of events seems convincing, given the fact that since then neither the political nor the military Russian leadership has given any clear comments on the topic of why Russia needed the data landing ships.
Returning to the PRC, it can be noted that the political leadership in Beijing from the very beginning rejected the very idea of political and economic isolation of Moscow in connection with the tragic events that unfolded in Ukraine. Even on the situation with the return of the Crimean peninsula, China spoke out quite openly and with a straightforwardness unusual for Chinese politicians. Director of the Department of Europe and Central Asia of the Chinese Foreign Ministry Gui Cunyun said: “China is against any nation gaining independence through a referendum. If we talk about Crimea, then it has its own characteristics. We know Crimea very well.”

RIA Novosti infographics
This was followed by a statement by Zhou Li, deputy head of the Department of International Relations of the CPC Central Committee, who noted: “Russia and the PRC are facing various challenges today. However, I can say with confidence that in the near future we will face more a large number calls. We must fight together to protect the interests of our states. The main thing is not to allow a wedge to be driven between our states, which the Americans would really like to do.” In the current environment, such support at the international level is expensive. Perhaps even the S-400 Triumph can be risked. After all, Russia has a more promising complex on the way - the powerful S-500 Prometheus anti-aircraft missile system.
S-400 will cover priority targets in China
According to Simon Wezeman, first of all, the S-400 systems purchased from Russia will be located at priority facilities in China, which include the country’s key military and administrative centers, which are currently protected by the Russian S-300 air defense systems and Chinese HQ -9. The S-400 is effective in repelling attacks from cruise and operational-tactical missiles, which pose the main threat to such centers, the expert believes.
“These complexes are able to reliably destroy a variety of targets - from enemy cruise missiles to strategic bombers, including those built using stealth technology,” says Igor Korotchenko, editor-in-chief of the magazine “ National Defense" “I believe that there are two main areas for using the S-400 Triumph: they will cover Beijing, as the country’s largest political center, as well as one of the coastal areas. The PRC, purchasing S-400 systems from Russia, is making good investments in ensuring its national security,” noted Igor Korotchenko. Previously, information appeared in the Chinese press that new Russian complexes Air defense can be used to cover the country's airspace in potentially dangerous directions from Japan, Vietnam, South Korea and Taiwan.

RIA Novosti infographics
According to Vasily Kashin, an expert at the Center for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies (Russia), the PRC will not be supplied with the basic configuration for the Russian army, but with “heavy” missiles with a firing range of up to 400 km. These missiles will allow China to shoot down air targets over the East China Sea. “These missiles will make it possible to hit air targets in the Diaoyu Islands from the Chinese mainland,” explained Vasily Kashin.
In turn, Simon Wezeman believes that the increased firing range of the S-400 missiles will allow China to cover the Taiwan Strait and part of the airspace over the island itself. “Thus, China will gain an advantage in possible armed conflicts in the Taiwan area, as well as in parts of the South China and East China Seas,” Wezeman noted. According to a foreign military expert, such an air defense system in the hands of China is capable of changing the balance of power in the region, although such a change will not be dramatic.
Simon Wezeman believes that other states in the region will try to find opportunities to neutralize the advantages of the S-400, just as they did previously after Beijing’s purchase modern systems weapons. For example, using long-range missiles with an anti-radar system, means electronic warfare And the latest aircraft, made using stealth technology.

The S-400 complex in service with the Russian army
The S-400 anti-aircraft missile system was created by the Russian air defense concern Almaz-Antey on the basis of their other long-range air defense system - the S-300. China was also one of the main foreign buyers of the previous complex. In total, the People's Liberation Army of the People's Republic of China acquired 15 S-300 divisions, the contract was completed in 2010. Now Beijing has decided to once again rely on Russian weapons, this time on the S-400.
It is worth noting that currently in full swing The Russian armed forces are becoming saturated with this complex. The last regiment equipped with the S-400 air defense system was deployed to Kamchatka. In April 2015, sea transport with 40 units of equipment from the regimental set of this air defense system arrived at the port of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. The complexes will be deployed at duty positions near the cities of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky and Vilyuchinsk. They must replace the S-300 air defense systems on combat duty.
The modern S-400 air defense system is truly unique. It can confidently destroy not only enemy aircraft, but also cruise and operational-tactical missiles at a distance of up to several hundred kilometers. During tests of the S-400 at the Ashuluk and Kapustin Yar test sites, the crews of the complex managed to shoot down a target with one missile that was moving at a speed of 2800 m/s, and with another missile they hit a target that was at an altitude of 56 km.

The S-400 complex allows you to simultaneously fire at up to 36 air targets, aiming up to 72 missiles at them. In the west, the complex received the designation SA-21 Growler (“Growler”). A wide range of missiles can be used with this air defense system, including those from previous systems. Three of them - missiles 48N6E, 48N6E2 and 48N6E3 - are suitable for live firing with both the S-400 and the S-300PM version. The 48N6DM missile was created specifically for the S-400 Typhoon. These missiles are controlled according to the principle of semi-active radar homing with correction. Also, the Russian industry is preparing to release two more missiles - 9M96E and 9M96E2, which will use the method of active radar homing to a target.
Application various types anti-aircraft missiles allows you to create a layered air defense system using the S-400. At the same time, the Triumph system is ready to simultaneously solve the tasks of both air defense and non-strategic missile defense. And the automation tools used in this air defense system almost completely eliminate errors caused by the so-called human factor.
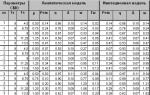
As of December 2014, 9 regiments (19 divisions) of S-400 complexes were deployed in Russia. One regiment is deployed in three divisions. Plans for 2015 previously called for the deployment of the S-400 Triumph air defense system near Novosibirsk (summer 2015), as well as on the archipelago New Earth. In total, by 2020, the Russian Ministry of Defense expects to receive 56 S-400 divisions, while 4 S-400 regiments should be allocated for the defense of Moscow. Each deployed division consists of 8 launchers.
Currently deployed 9 regiments/19 divisions/152 launchers:
2 divisions in Elektrostal (the first in 2007, the second in 2009), Moscow region.
2 divisions in Dmitrov (the regiment was deployed in 2011), Moscow region.
2 divisions in Zvenigorod (the regiment was deployed in 2012), Moscow region.
2 divisions in Nakhodka (the regiment was deployed in 2012).
2 divisions in the Kaliningrad region (regiment deployed in 2013)
2 divisions in Novorossiysk (the regiment was deployed in 2013).
2 divisions in Podolsk (the regiment was deployed in 2014), the 4th regiment in the Moscow region.
2 divisions on the Kola Peninsula (the regiment was deployed in 2014-2015).
3 divisions in Kamchatka (the regiment was deployed in 2014-2015).
Sources of information:
http://svpressa.ru/war21/article/118647
http://lenta.ru/news/2015/04/13/s400
http://ria.ru/world/20150413/1058317195.html
http://www.rg.ru/2015/04/13/triumf-site.html
MOSCOW, September 15 - RIA Novosti, Andrey Stanavov. Intercepting aircraft and ICBM warheads at altitudes of up to 27 kilometers, instant deployment and about a hundred simultaneously guided anti-aircraft missiles - the unique S-400 Triumph system will destroy ballistic targets during the Zapad-2017 exercises. Signed with NATO member Turkey, Triumph caused a stir in Russian and Western media. According to The National Interest magazine, this deal will give the alliance the most modern Russian technologies in the field of air defense and will allow us to develop an effective “antidote” for them. However, not everything is so simple. Read about what they say about the S-400 system in the West and why its main secrets will not leave Russia’s borders in the RIA Novosti material.
Demo version for NATO
The S-400 Triumph mobile multi-channel anti-aircraft missile system (AAMS) is the pride of Russian developers. Back in 2007, the complex, which was put into service, is capable of effectively “removing” from the sky all modern and promising aerospace attack weapons, including those flying at speeds of up to five kilometers per second.
There is no escape from it in the air - airplanes and cruise missiles are reliably eliminated at a range of up to 250 kilometers, ballistic missiles - up to 60 kilometers. From traveling position to combat system unfolds in three minutes. "Triumph" can simultaneously conduct up to 300 targets and fire up to 72 missiles at them. Despite the fact that military experts often compare the S-400 system with the American Patriot complex, it is hopelessly inferior to it in many respects.
The supply of such weapons for export, and especially to a NATO country, often causes waves of discussions about the possible leak of secret defense technologies and damage to national security. Even at the stage of preparing the contract, analysts from The National Interest magazine openly stated that Turkey’s purchase of the S-400 would provide NATO with valuable data on the operational capabilities of the system and would allow it to develop means to neutralize it. According to the author of the article, even “a degraded export version of the S-400 will provide the West with information on how to defeat the latest tools Russian air defense."
However, Russian military expert, editor-in-chief of the Arsenal of the Fatherland magazine, Colonel Viktor Murakhovsky, called this statement “incompetent chatter,” citing the fact that export models are significantly inferior in combat characteristics to those in service Russian army and carefully “freed” from latest technologies protected by state secrets.
“The preparation of an export passport is controlled by the structure of the Ministry of Defense - the Federal Service for Military-Technical Cooperation. Without a visa from the defense department, not a single product will go abroad in a configuration that poses a threat to the national security of Russia. The same applies to the S-400 complex,” Murakhovsky said RIA Novosti.
The expert recalled that some NATO countries already have Russian-made anti-aircraft systems, and Turkey will not be a pioneer in this. In particular, according to him, Greece has been operating the S-300 and Buk air defense systems for a long time, and no complications have ever arisen.
"Take it apart piece by piece"
As for the export of S-400s, to date, apart from Turkey, Russia has signed a contract for their supply only with China. The deal was officially announced in April 2015. The PRC intends to purchase three regimental sets - up to 48 launchers. Deliveries should begin this year. In addition, negotiations are underway with India on the purchase of five regimental sets (up to 80 launchers). The country's Defense Acquisition Council approved the deal in December 2015. The parties are still discussing details.
“All fears about technology leaks are greatly exaggerated, especially in the area that relates to anti-aircraft missile weapons,” says Mikhail Khodarenok, editor-in-chief of the Aerospace Frontier magazine. “Even if they disassemble the system piece by piece and try to extract from it what "The military secrets, I think, will be left with nothing. Again, such a system was delivered to China, and it was probably dismantled there."
At the same time, Mikhail Khodarenok emphasized that, even despite the reduction of some functions, the export Triumph as a whole will retain its combat potential and Turkey will acquire one of the most modern defensive systems in the world, capable of sealing the country's airspace with a secure lock.
The sky is under control: S-400 Triumph air defense systems deployed in the Moscow regionAn anti-aircraft missile regiment, equipped with the new S-400 Triumph air defense system, took up combat duty in the air defense system of Moscow and the center of Russia. Watch the video as it unfolds military equipment in the Moscow region.“Turkey’s main rival in the region is Iran,” said Andrei Frolov. “The Islamic Republic has a fairly powerful Air Force. At the same time, Iran can protect itself from a possible retaliatory strike: last year Russia supplied it with four divisions of S-300PMU2 complexes. In addition, Ankara, to put it mildly, has tense relations with Damascus, which is armed with long-range tactical and operational-tactical missiles, and Turkey’s air defense systems are frankly weak.”
To date, the Turkish Armed Forces do not have long-range anti-aircraft missile systems as a class. The country's air force is now equipped anti-aircraft missile systems medium-range MIM-14 and MIM-23 manufactured in the USA and British short-range air defense systems Rapier. These systems were developed back in the 50-60s of the last century and are considered obsolete today.
The first visit to Russia by the King of Saudi Arabia may result in the conclusion of a package of arms contracts worth over $3 billion, implying the supply of S-400 Triumph anti-aircraft missile systems to Riyadh.
For the first visit to Moscow by the King of Saudi Arabia, Salman bin Abdulaziz al-Saud, in the history of bilateral relations, the Russian side has prepared a package of contracts, including in the defense sector. In particular, we are talking about supplies to the Saudis of S-400 systems worth about $3 billion.
As experts note, if the negotiations between the King of Saudi Arabia and the President of Russia are positive, the contract for the supply of Triumphs may be signed during the meeting of the Russian-Saudi intergovernmental commission on military-technical cooperation, which is scheduled for the end of October.
In this case, Saudi Arabia will become the second foreign buyer of the S-400 after Turkey, with which the contract was signed in September. Moreover, by the end of the year a contract for the supply of Triumphs to India may be concluded: according to unofficial information, all preparatory work on this issue has already been completed.
In total, Russia has already received about a dozen applications for the supply of S-400. This, in particular, was stated in an August interview with Kommersant by the head Federal service on military-technical cooperation Dmitry Shugaev.
The S-400 Triumph anti-aircraft missile system is designed to destroy strategic and tactical aircraft, ballistic missiles and other air attack weapons. It includes a combat command post with radar complex detection, all-altitude radar, up to six anti-aircraft missile systems, anti-aircraft guided missiles of two types.
Export contracts for Triumphs are, first of all, a big breakthrough for the system manufacturer, namely the Almaz-Antey VKO concern. It should be noted that for the third year the concern has been in 11th place in the ranking of the world's leading weapons manufacturers, which is compiled by the weekly Defense News.
Thanks to new contracts, S-400 manufacturers will be able to improve their position in the ranking, overtaking the French company Thales (10th place), and perhaps even the American L-3 Communications (9th place) and the Italian Leonardo Spa (8th place) . However, for this you will have to wait a couple of years: as experts explain, the Triumph production cycle is two years, so the contracts concluded now will be fulfilled only by the beginning of 2020.
The new 3 billion contract will look impressive on the scale of overall Russian arms exports. Let us remember that last year our arms exports exceeded $15 billion compared to $14.5 billion in 2015. At the same time, new contracts were concluded for $9.5 billion, as a result, the total portfolio of military export orders remained at the level of 50 billion.
Analysts note that last year the main emphasis of Russian gunsmiths was on the implementation of already concluded contracts - the supply of Su-35 fighters and Ka-32A11BC helicopters to China, MiG-29K carrier-based fighters to India, diesel-electric submarines project 06361 "Varshavyanka" to Vietnam, etc., as well as on marketing, which was based, among other things, on the results of the use of our military aviation and air defense systems in Syria.
In 2017, the defense export system will reap the benefits of this work. In the coming months, contracts are expected for deep modernization of the most massive combat aircraft Indian Air Force - Su-30MKI fighter and the delivery of two Varshavyanka submarines to Indonesia. In addition, substantive negotiations are underway on the supply of Su-35 fighters to Indonesia, and Su-32 bombers (export version of the Su-34) to Algeria.
In the summer, even before the Triumph contracts with Turkey and Saudi Arabia, analysts predicted the volume Russian exports arms at the end of 2017 at 14–15 billion dollars for supplies and 6–17 billion for new contracts. For comparison, according to the forecast of the British military analytical publication Jane's, US military exports this year will amount to $26.9 billion.