To use preview presentations create yourself an account ( account) Google and log in: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Fuel and energy complex of Russia. Oil and gas industry. Presentation for a geography lesson in 9th grade. Textbook by V.P. Dronov. V.Ya.Rom., teacher of secondary school No. 1 in Kondopoga, Svetlana Anatolyevna Sidorkova
Purpose of the lesson. 1. Find out the meaning and composition of fuel and energy complex. 2.Give the concept of fuel and energy balance. 2. Study the fuel industry, consider the most important deposits of fuel minerals in Russia, large bases, methods of extraction and transportation of fuel. 3. Factors for locating enterprises in industries fuel industry. 4.Prospects and problems of development of the complex.
Fuel and energy complex Fuel industry Electric power industry Production infrastructure oil thermal power plant, hydroelectric power station, nuclear power plant power lines gas oil pipelines coal gas pipelines peat
The task of the fuel and energy complex is Extraction of fuel, production of electricity and their transmission to the consumer.
The ratio of fuel production and generated electricity (income) and their use in the country’s economy (consumption) Fuel and energy balance
Oil industry Crude oil It is explosive and is almost never used. Gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, and fuel oil are produced from oil. Plastics, polymers, and chemical fibers are produced from oil. Oil is extracted in two ways: flowing and pumping. D
Oil fields
Working with the map. Find the deposit data on the map. Mark them on the contour map. 70% of Russian oil is produced in Western Siberia. (Samotlor, Megion) 25% Volga-Ural base (Romashkinskoye field, Ishimbayevskoye) Promising fields. Shelf Barents Sea and Sakhalin Islands.
Oil transportation Via oil pipelines Oil tankers
The largest oil pipeline - Druzhba
Druzhba is the world's largest oil trunk pipeline system. Built in the 1960s by the USSR enterprise Lengazspetsstroy to deliver oil from the Volga Ural oil and gas region to the socialist countries of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (CMEA): Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Poland and the German Democratic Republic, located in Eastern Europe.
Largest oil and gas basins
Refineries are oil refineries. They are located in areas where products are consumed!!! List the largest refineries from the atlas map
Gas industry Gas is a cheap and environmentally friendly high-calorie fuel.
The most important fields 92% of gas is produced in Western Siberia (Urengoy, Yamburg, Medvezhye) 6% Orenburg-Astrakhan base 1% Timan-Pechora base In terms of gas reserves and production, Russia ranks first in the world!!!
Gas is transported through gas pipelines
Yamal-Europe, Blue Stream, South Stream, Nord Stream. Find on the map.
Consolidation of material 1. What industries are included in the fuel and energy complex? 2.What is the fuel and energy balance? 3.What are the methods of oil production? Why are refineries not built in mining areas, and in areas where products are consumed?
Preview:
Geography lesson in 9th grade. Fuel and energy complex. Oil and gas industry.
Teachers of Municipal Educational Institution Secondary School 1 in Kondopoga Svetlana Anatolyevna Sidorkova
Lesson objectives:
Educational
- introduce students to the features of the Russian fuel and energy complex;
- find out the composition of the fuel industry;
- identify the main fuel bases, promising areas for gas and oil production, methods of production and transportation of fuel
Educational:
- develop communication skills (drawing up lecture abstracts);
- develop logical thinking, the ability to work with a map, draw conclusions
Educational
- Structure of the Fuel and Energy Complex.
- The importance of the fuel and energy complex in the Russian economy.
- Structure of fuel and energy production in Russia.
- Fuel industry of Russia: coal, oil, gas.
- The current level of development of the fuel and energy complex. By regions of Russia.
- Features of the Russian electric power industry.
- Structure of electricity production in Russia.
Literature:
- Geography of Russia. Population and economy: textbook, Dronov V.P. – M.: Bustard, 2010.
- Statistical Review of World Energy 2010
- "Industry of Russia", 2010
Slide 2
1. Fuel and energy complex (FEC)
- is a complex inter-industry system of extraction and processing of fuel, production of electricity, their distribution, transportation and delivery to the consumer. It includes the fuel industry and electricity.
Slide 3
Structure of the fuel and energy complex
Slide 4
2. Fuel and energy complex is the leading inter-industry complex in Russia
- it provides 30% of GDP (as of 2009). Fuel and energy products are the main export item of Russia (about 66% in 2009) and provide a significant portion of foreign exchange earnings. In addition, the fuel and energy complex ensures the development of other sectors of the country's economy, providing them with fuel and energy.
Slide 5
3. Structure of fuel and energy production in Russia for 2009.
- For comparison (worldwide): oil - 34.1 coal - 29.6 gas - 26.5 HPP - 5.2 NPP - 4.6
Slide 6
4. Fuel industry of Russia
- Oil industry
- Gas industry
- Coal industry
- Uranium industry
- Others (oil shale, peat)
Slide 7
Features of the Russian coal industry
- Russia ranks 2nd in the world in terms of proven coal reserves
- Russia ranks 6th in coal production (2009);
- 71% of coal mined in Russia is hard and 29% is brown;
- Russia is one of the largest coal exporters (6th place);
- ¾ of the coal mined for own consumption is used as fuel in thermal power plants, and ¼ is used as technological raw material in chemical industry and fuel in metallurgy
- The main disadvantage coal deposits Russia is their uneven distribution throughout the country
Slide 8
- European part 18%
- Ural 7%
- Siberia 64%
- Far East 12%
- Territorial distribution of coal reserves in Russia
Slide 9
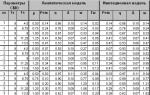
Dynamics of changes in production capacity and coal production volumes
Slide 10
Distribution of coal production by basin for 2009.
Slide 11
Features of Russian coal basins
- The Kuznetsk basin is located in the Kemerovo region. Coal is mined here high quality. This pool requires large capital investments, since most mines built during the pre-war five-year plans are in need of reconstruction. 42% of coal here is mined by open-pit mining. The main disadvantage of this basin is its significant distance from the main consumption areas.
- The Kansk-Achinsky basin is located near the Kuznetsk basin in the territory Krasnoyarsk Territory. Mined here brown coal. This is one of the youngest coal mining areas. Coal is mined here by open-pit mining, so its cost is the lowest in Russia. However, the quality of coal is quite low (40% ash, high sulfur) and its transportation is inefficient; coal from this basin is used locally as fuel for thermal power plants
- The Pechora basin is located in the north of the Komi Republic, in the Vorkuta region. High quality coal. This pool began to be actively developed during the Great Patriotic War, after the capture of Donbass by fascist troops. Currently, its share in coal mining is constantly declining. The main reason for this is the high cost of production (mine mining method + difficult climatic conditions). In addition, this basin is quite remote from the main consumers, so the consumption of its coal is mainly limited to the European North of Russia
Slide 12
- The Irkutsk (Cheremkhovo basin) began to develop even before the revolution to supply fuel to steam locomotives Trans-Siberian Railway. Open method 4.5% of Russian coal is mined here. The cost of coal is quite low. The importance of this basin is great for supplying thermal power plants and boiler houses in the cities of Eastern Siberia.
- The South Yakut basin has rich reserves of coking coal. About 4% of the country's coal is mined here, a significant part of which is exported to Japan
- Most of the Donetsk basin is located in Ukraine, and a smaller part is in Russia, in the west of the Rostov region. This coal basin in Russia produces about 2% of high-quality coal, although the coal lies deep and in thin layers
- Coal mining in the Moscow basin (Tula region) is of local and decreasing importance (0.5%), since the quality of coal is low
Slide 13
Subjects of the Russian Federation are leaders in coal production
Slide 14
Features of the Russian oil industry
- In terms of proven oil reserves (more than 10 billion tons in 2009), Russia ranks sixth in the world. Currently, Russia ranks first in oil production (494 million tons in 2009), ahead of Saudi Arabia
- Russia ranks first in oil exports (more than 300 million tons per year)
Slide 15
Dynamics of oil production in Russia
Slide 16
Distribution of oil production by basins
Slide 17
Subjects of the Russian Federation are leaders in oil production
Slide 18
Features of the Russian oil refining industry
- Refineries are located mainly in consumption areas
- The main disadvantage of the oil refining industry is the high level of concentration. There are only 26 oil refineries in Russia, of which 20 are located in the European part. Although it's quite large enterprises(average capacity 12 million tons per year) and in terms of their total capacity (300 million tons per year) they can fully meet the needs of Russia, but they are often significantly removed from the consumer. For comparison: in the USA there are 190 refineries with an average capacity of 3-5 million tons per year
Slide 19
Features of the Russian gas industry
- Russia ranks first in the world in gas reserves, production and exports;
- 93.7% of the produced gas is natural, 6.3% is associated petroleum.
- There are about 700 explored gas fields in Russia
- Among consumers of Russian gas, the share of foreign European countries is growing at the fastest pace, while the share of CIS countries is decreasing
Slide 20
Dynamics of gas production in Russia
Slide 21
Distribution of gas production by region
Slide 22
Subjects of the Russian Federation are leaders in gas production
Slide 23
5. Subjects of the Russian Federation are leaders in the fuel industry
- Tyumen region – 51%
- Tatarstan – 7.4%
- Bashkortostan – 5.4%
- Kemerovo region – 4.2%
Slide 24
Economic regions are leaders in the fuel industry
- West Siberian – 56.4%
- Ural – 13.5%
- Povolzhsky – 12.8%
- Northern – 4.3%
- Central - 4.3% (mainly due to the processing industry, the fuel industry is not a sector of the region’s specialization)
Fuel and energy complex (FEC)
Plan for studying a new topic:
- Composition of fuel and energy complex
- Fuel and energy balance
- Energy saving technologies

Fuel and energy complex - a set of industries related to the production and distribution of energy in its various types and forms .

Determine which 3 links are included in the fuel and energy complex?
Inserting a picture
Transport of heat, fuel, electricity

The entire economy of the country depends on the development of the fuel and energy complex
Share
fuel and energy resources in Russia's exports amount to about 40%
Why?

Fuel and energy balance- ratio of production of various types of fuel and generated energy (reception part) and their use on the farm (exhaustive part)
- To compile the fuel and energy balance, various types of fuel are converted into conventional fuel (conventional fuel), the calorific value of 1 kg of which is equal to 7000 kcal. When converting into equivalent fuel, so-called thermal coefficients are used, by which the amount of the type of fuel being converted is multiplied. So, oil and natural gas this coefficient is 1.5; for coal - 1; for peat - 0.5, etc.
- Electricity generated at hydroelectric and nuclear power plants is converted into standard fuel at the rate of 1 ton of cu. t. - 2-3 thousand kWh of electricity (depending on the efficiency of the power plant).

- Fuel extraction and energy production in Russia are becoming increasingly expensive - new deposits are located in sparsely populated areas with harsh natural conditions;
- the costs of transporting fuel and energy are constantly increasing;
- Energy growth has a negative impact on the environment.

How can you save energy?
In Russia, energy-saving technologies have not yet received proper application, although the opportunities for savings are truly enormous.
Inserting a picture
Only by improving the thermal insulation of buildings and using economical lighting sources can tens of millions of tons of fuel be saved annually.

Homework
Questions on a new topic.
1. What is included in the fuel and energy complex?
2. What is the fuel and energy balance?
3. Why is it important to save energy?
Fig. 33-34 - analysis