Air defense index - 40Р6
According to the codification of the US Department of Defense and NATO - SA-21 Growler, literally “Growler”
Russian anti-aircraft missile system long and medium range, new generation anti-aircraft missile system (SAM). Designed to destroy all modern and promising means of aerospace attack. On April 28, 2007, by decree of the Government of the Russian Federation, the Triumph air defense system was put into service.

Description
The complex is capable of hitting aerodynamic targets at a range of up to 400 km and tactical ballistic targets flying at a speed of up to 4.8 km/s at a range of up to 60 km: cruise missiles, tactical and strategic aircraft, ballistic missile warheads. The early warning radar provides a detection range of up to 600 km. The missiles are capable of destroying low-flying targets at an altitude of 5 m (for comparison: the American Patriot complex is capable of hitting targets only at an altitude of at least 60 m). It is possible to use several types of missiles with different launch masses and launch ranges, which makes it possible to create a layered defense.

According to the Air Force Commander-in-Chief, “they can effectively repel massive raids by modern air attack weapons in conditions of intense electronic suppression and carry out combat mission in various weather conditions."
The control equipment includes a digital control system of the Elbrus-90micro series. The main developer is NPO Almaz named after. Academician A. A. Raspletin. General designer - Alexander Lemansky.

In the future, it may become the basis for a missile defense system.
Composition of the 40Р6 (S-400) system
1. 30K6E controls consisting of:
-Combat control point (PBU) 55K6E based on Ural-5323 01.
-Radar complex (RLK) 91Н6E. Panoramic radar with interference protection. installed on MZKT-7930. Operates in the UHF range.

2. Up to 6 anti-aircraft missile systems 98Х6Э. A maximum of 10 targets with 20 missiles aimed at them, each consisting of:
-Multifunctional radar (MRLS) 92N2E with a range of 400 km. 100 targets.
-Up to 12 transport-launch units (TLU) of type 5P85TE2 and/or 5P85SE2 on a trailer.

3. Anti-aircraft missiles 48N6E, 48N6E2, 48N6E3 of the existing S-300PMU1, ?2 air defense systems, as well as 9M96E and 9M96E2 missiles and the 40N6E ultra-long-range missile.
4. Complex of funds technical support systems 30TS6E.
Proprietary S-400 radar systems: anti-jamming all-round radar with two-way phased active array (PAR)
Possible elements of S-400 (98ZH6E): 15I6ME - for moving to a distance of 98ZH6E 30/60/90 km from 30K6E. All-altitude detector 96L6E - universal complex (all functions), detection range 300 km. 40B6M - tower for 92N6E or 96L6E. Anti-stealth radars: Opponent-GE, Gamma-DE. Passive sensor (locator) for target designation for air defense systems Orion (coordinates 1 of 3), Avtobaza-M passive sensor (locator) for target designation for air defense systems (coordinates 2 remaining of 3). It is possible to use S-200D "Dubna" missiles 400 km. As well as various (P versions) S-300 radar system without participation additional centers management and control. It is possible to use S-300 missiles. A-50 / 50U Early warning aircraft, command and transfer of target designation control.

The 30K6E control system can control:
System S-400 Triumph 98ZH6E;
-S-300PMU2 (via 83M6E2 control system);
-S-300PMU1 (via 83M6E control system);
-Tor-M1 via Ranzhir-M mobile command post;

Pantsir-S1 via KP Pantsir;

Radar 96L6E / 30K6E system administration, Opponent-GE, Gamma-DE. Possibility of integration with 92H6E radar system provision from each battery for:
Baikal-E senior command posts and other similar ones;
-In the accessibility zone (30-40 km) 30K6E, 83M6E and 83M6E2 control systems;
-Polyana-D4M1 command post;
-Air Force command post.
For export deliveries in coordination with foreign customers, equipment is possible for the purpose of integration into customer protection systems of the 30K6E control system.

Components
Maximum range for detection. For a ballistic target (velocity 4800 m/s and effective dispersion area 0.4 m2): 230 km. For a target with an EPR of 4 m2: 390 km. For orientation of strategic aircraft: 570 km.
The maximum altitude for target detection is 100 km in any direction. You can use tower 966AA14. High capabilities against cruise missiles and stealth. Radar with multi-beam phased array antenna 96L6E radar and hardware unit at a distance of 100 m, 96L6E2 export version. 100 targets. Independent of signal reflection by mountains. Replaces the radar with low-altitude radar and all-round visibility and sectors, not excluding stealth. Can serve as a command post for S-300 or S-400 battalions. 96L6-1 from S-400 and S-500. The maximum altitude for target detection is 100 km in any direction. You can use tower 966AA14. High capabilities against cruise missiles and stealth. Multibeam phased array radar

Command center PBU 55K6E
Automatic operation, serves as a command center for the entire system (all battalions and all external resources, including passive ones). The maximum distance between the command center and the 98ZH6E battalion using repeaters is up to 100 km.

Launchers 5P85TE2/5P85SE2 on a trailer.
5P85TE2 launchers and/or 5P85SE2 on a trailer in combination with a BAZ-64022 or MAZ-543 M tractor with a trailer. Possibility of free movement on the ground. Fuel consumption - 35%. The total cost of the launch vehicle is 25% (the cost of cars in 2014 was 8.7 million rubles)

Rockets
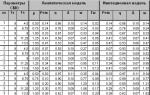
A special order of the President of the Russian Federation revealed five indices of anti-aircraft missiles that the S-400 air defense system can launch - 48N6E, 48N6E2, 48N6EZ, 9M96E2, 40N6E.



GRAU index |
Year |
Range, km |
Heights, km |
Engine operating time, sec. |
Maximum speed, m/s |
Speed of targets hit, m/s |
Length, m |
Diameter, mm |
Weight, kg |
Weight of warhead, kg |
Control |
| 48Н6E/ 48Н6 | 1992 | 150 | 12 | until 2100 | 7,5 | 519 | 1800-1900 | 143-145 | |||
| 48Н6E2/ 48Н6М | 1992 | 200 | until 2100 | 2800 | 7,5 | 519 | 1800-1900 | 150 | Semi-active radar homing with radio correction | ||
| 48N6E3/ 48N6-2/ 48N6DM | ? | 250 | 0,01-27 | up to 2500, average 1340 | 4800 | 7,5 | 519 | 1800-1900 | 180 | Semi-active radar homing with radio correction | |
| 9M96E2/ 9M96M non-export | 1999 | 120/1-135 | 0,005-30/0,005-35 | 1000 | 240 | 420 | 24 | ||||
| 9M96E | 40 | 20 | 333 | Active radar homing | |||||||
| 40N6E | 2015 | up to 400 | 185 | Active/semi-active homing |
The 9M96M missile, when launching one missile, provides a probability of intercepting a tactical aircraft - 0.9, and a UAV - 0.8. Capable of maneuvering with an overload of 20G at an altitude of up to 35 km, which significantly increases the ability to intercept medium and short-range ballistic missiles. Maximum overload in a maneuver is 22G for 48Н6E3, warhead weight is 180 kg.
Tests
On July 12-13, 2007, target shooting was carried out at the Kapustin Yar training ground. The first target was shot down at a speed of 2800 m/s, the second Kaban target missile was detected and then destroyed at an altitude of 16 km.

February 18, 2011 during the inspection new technology Two S-400 divisions of the 210th anti-aircraft missile regiment took part, and the target was destroyed at a speed of 550 m/s.
In August 2013, tests of the S-400 were carried out for the first time as part of a tactical exercise.

Deployment
Deployment in Russia
On August 6, 2007, in the city of Elektrostal, Moscow Region, the first division armed with the S-400 Triumph anti-aircraft missile system (ZRS) took up combat duty. In 2009, a second division was added to it, which together with the first formed the 606th Guards Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment (16 launchers in total).

On May 16, 2011, the second regiment equipped with the S-400 air defense system, the 210th anti-aircraft missile regiment in the city of Dmitrov (2 divisions, each with 8 launchers), took up duty.
According to data as of January 29, 2014, only 5 S-400 regiments were formed, namely: in the Moscow region, in the Baltic and Pacific Fleet and in the Southern Military District. Each regiment includes two S-400 divisions with eight launchers each.
12 regiments / 25 divisions / 200 launchers for 2015 deployed:
1. 2 divisions in 4 DPVO VVKO 606 zrp (Elektrostal) Mos. region, (in 2007 the first division was deployed, in 2009 the second division was installed);
2. 2 divisions in 5 DPVO VVKO 210 air defense division (Dmitrov) Mos. region, (deployed in 2011);
3. 2 divisions in 5 DPVO VVKO 93 air defense division (Zvenigorod) Mos. region, (deployed in 2012);
4. 2 divisions in the 93 DPVO 589 air defense and air defense air defense (Nakhodka) (deployed in 2012);
5. 2 divisions in 44 DPVO 183 air defense regiment BF (Kaliningrad) (deployed in 2013);
6. 2 divisions in 51 DPVO 1537 air defense and air defense air defense (Novorossiysk) (deployed in 2013);

7. 2 divisions in 4 DPVO 549 air defense division VVKO (Kurilovo) Mos. region, 4th regiment in the Moscow region (deployed in 2014);
8. 2 divisions in 1 DPVO 531 air defense missile system USC "Sever" (Polyarny) (deployed in 2014);
9. 3 divisions in 53 DPVO 1532 air defense missile defense Pacific Fleet (Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky), differs from previously delivered by the presence of 24 launchers (3 divisions), deployed in 2015;
10. 2 divisions in 41 DPVO 590 air defense and air defense air defense (Novosibirsk) (the first regimental set, delivered in 2015);
11. 2 divisions in the 2nd air defense division ( Leningrad region) (second regimental set, delivered in 2015);
12. 2 divisions in 93 DPVO 1533 air defense and air defense air defense (Vladivostok) (third regimental set, delivered in 2015)
There are plans to deploy the S-400 Triumph air defense system on the Novaya Zemlya archipelago.

According to plans, 5 regimental sets will be delivered in 2016.
In total, 56 divisions are planned to be acquired by 2020; for the defense of Moscow up to four S-400 regiments by 2020 (the fourth regiment in the Moscow region was deployed already in 2014). Armed forces Starting in 2014, Russia will receive two or three regimental sets of S-400 anti-aircraft missile systems per year at an increasing rate. It is planned to purchase 28 regimental sets of S-400.

Deployment in Syria
On November 26, 2015, the S-400 anti-aircraft missile system was deployed in Syria at the Russian Khmeimim airbase in Latakia and went on duty. The transfer took place with the help of An-124 Ruslan military transport aircraft from one of the regiments near Moscow.

In service
Russia - 12 regiments / 25 divisions / 200 launchers as of December 1, 2015.
-Algeria - according to unconfirmed data, 3-4 regiments as of July 2015.
-China - the contract was officially announced in April 2015, deliveries are expected to begin in 2017.
-India - in November 2015, an agreement was announced to supply India with S-400 systems worth about $10 billion. The official conclusion of the contract is planned during the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Moscow, which is expected in December 2015.

Project evaluation
According to a study by the Australian think tank Air Power Australia, published in February 2009, the S-400 is significantly superior American systems Air defense Patriot.
On June 28, 2012, the commander of the air defense and missile defense forces of the aerospace defense of the Russian Federation, Major General Andrei Demin, said that the new long-range missile for the S-400 anti-aircraft missile systems has already been tested and will soon enter service with the troops.

| Maximum target speed, km/s | 4,8 |
| Detection range, km | 600 |
| Cover zone boundaries by range, km -maximum -minimum |
|
| Boundaries of the altitude cover zone from aerodynamic targets (2015, km) -maximum -minimum |
27 (any missiles) / 30 to 56 (2015, potentially up to 185) km (40N6) 0.005 (9M96) / 0.010 (any missiles) |
| Cover zone boundaries by range from all available ballistic missiles, km -maximum -minimum |
60 5 |
| Maximum targets fired at the same time | 80 (before 2012 - 36) |
| Maximum missiles aimed at targets | 160 |
| Readiness for combat upon receiving a command while on the move, minutes | 5 (in 2010 - 10-15) |
| Readiness, minutes | 0.6 from standby mode / deployed on terrain 3 |
| Continuous working hours | 10 000 |
| Service life, years -Components -Rocket |
minimum 20 15 |

| Russia |
The first visit to Russia by the King of Saudi Arabia may result in the conclusion of a package of arms contracts worth over $3 billion, implying the supply of S-400 Triumph anti-aircraft missile systems to Riyadh.
For the first visit to Moscow by the King of Saudi Arabia, Salman bin Abdulaziz al-Saud, in the history of bilateral relations, the Russian side has prepared a package of contracts, including in the defense sector. In particular, we are talking about supplies to the Saudis of S-400 systems worth about $3 billion.
As experts note, if the negotiations between the King of Saudi Arabia and the President of Russia are positive, the contract for the supply of Triumphs may be signed during the meeting of the Russian-Saudi intergovernmental commission on military-technical cooperation, which is scheduled for the end of October.
In this case, Saudi Arabia will become the second foreign buyer of the S-400 after Turkey, with which the contract was signed in September. Moreover, by the end of the year a contract for the supply of Triumphs to India may be concluded: according to unofficial information, all preparatory work on this issue has already been completed.
In total, Russia has already received about a dozen applications for the supply of S-400. This, in particular, was stated in an August interview with Kommersant by the head Federal service on military-technical cooperation Dmitry Shugaev.
The S-400 Triumph anti-aircraft missile system is designed to destroy strategic and tactical aircraft, ballistic missiles and other air attack weapons. It includes a combat command post with radar complex detection, all-altitude radar, up to six anti-aircraft missile systems, two types of anti-aircraft guided missiles.
Export contracts for Triumphs are, first of all, a big breakthrough for the system manufacturer, namely the Almaz-Antey VKO concern. It should be noted that for the third year the concern has been in 11th place in the ranking of the world's leading weapons manufacturers, which is compiled by the weekly Defense News.
Thanks to new contracts, S-400 manufacturers will be able to improve their position in the ranking, overtaking the French company Thales (10th place), and perhaps even the American L-3 Communications (9th place) and the Italian Leonardo Spa (8th place) . However, for this you will have to wait a couple of years: as experts explain, the Triumph production cycle is two years, so the contracts concluded now will be fulfilled only by the beginning of 2020.
The new 3 billion contract will look impressive on the scale of overall Russian arms exports. Let us recall that last year our arms exports exceeded $15 billion compared to $14.5 billion in 2015. At the same time, new contracts were concluded for $9.5 billion, as a result, the total portfolio of military export orders remained at the level of 50 billion.
Analysts note that last year the main emphasis of Russian gunsmiths was on the implementation of already concluded contracts - the supply of Su-35 fighters and Ka-32A11BC helicopters to China, MiG-29K carrier-based fighters to India, diesel-electric submarines project 06361 "Varshavyanka" to Vietnam, etc., as well as on marketing, which was based, among other things, on the results of the use of our military aviation and air defense systems in Syria.
In 2017, the defense export system will reap the benefits of this work. In the coming months, contracts are expected for deep modernization of the most massive combat aircraft Indian Air Force - Su-30MKI fighter and the delivery of two Varshavyanka submarines to Indonesia. In addition, substantive negotiations are underway on the supply of Su-35 fighters to Indonesia, and Su-32 bombers (export version of the Su-34) to Algeria.
In the summer, even before the Triumph contracts with Turkey and Saudi Arabia, analysts predicted the volume Russian exports arms at the end of 2017 at 14–15 billion dollars for supplies and 6–17 billion for new contracts. For comparison, according to the forecast of the British military analytical publication Jane's, US military exports this year will amount to $26.9 billion.
"Grumpy" for export
Why Türkiye will not get access to S-400 systems
Turkey will not have access to internal systems S-400: Gazeta.ru publication found that electronic codes from anti-aircraft missile system"Triumph" will remain with Moscow. Only Russian specialists will be able to repair equipment and carry out scheduled maintenance. More about, incl.
Why is this needed and how does the export S-400 differ from the original model? Alexey Sokolov.
The S-400 Triumph systems, which foreign militaries call “Grunts,” are highly coveted abroad. The characteristics are captivating - the early warning radar sees aircraft and ballistic missiles 600 km away, and after the 400 mark you can fire to kill. Experts say that the air defense systems have no analogues yet and are definitely superior to the American Patriot systems that were previously in Turkey. During the presidency of Barack Obama, the States took their air defense systems out of the country for maintenance; the Patriots never returned.
| Audio version |
The functionality of S-400s exported to Turkey is already limited, he says editor-in-chief magazine "Arms Export" Andrey Frolov.
“I think this issue has already been discussed on the Turkish side - although there were reports that they are going to produce it themselves, this production will probably concern hardware, not software. And, accordingly, in the case of hour X there is indeed an opportunity to make this complex unprepared for combat use- we lose little, because the system that will be supplied exists in export form, with roughened characteristics. Reduced number of tracked targets, noise immunity, range radar operation, rockets. All other systems that we exported were worse than what was supplied to the Russian army."
Earlier, Western media claimed that Turkey would refuse to purchase the S-400 due to possible difficulties in the interaction of the complexes with NATO radars. But back in March, Russian Presidential Assistant for Military-Technical Cooperation Vladimir Kozhin stated that Moscow sees no obstacles to the possible supply of air defense systems to Turkey due to its membership in NATO. Mr. Kozhin emphasized: the supply agreement is very strictly regulated, and each party assumes obligations about what it has the right to do with the supplied weapons and what not.
Turkey's membership in NATO is one of the main reasons why the country will not receive full access to the systems, says Sergei Denisentsev, an expert at the Center for Analysis, Strategies and Technologies:
“You need to understand that the “friend or foe” system used in Russia differs from that used in NATO countries. The need to exclude the copying of signals from the transponder of the “friend or foe” system is very important in order to exclude the possibility of the enemy using this system in the event of some kind of conflict.”
Previously, Türkiye planned to buy an air defense system from China for $4 billion, but the deal did not take place at NATO’s request. The amount that Ankara will pay for the Triumphs was not stated, but, according to Kommersant, the possible value of the contract with Russia is more than $2 billion for four S-400 divisions.
Deliveries of the S-400 to Turkey should begin within two years.
The West, especially the USA and Germany, reacts extremely nervously to the possibility of supplying S-400 systems to Turkey. Some politicians even declare the need to introduce anti-Turkish sanctions and expel Ankara from NATO. Why does Türkiye want to buy Russian complexes Air defense and why is Washington so nervous about it?
“This news, the game that Türkiye is playing with a potential systems supplier, is not new. It can be assumed that these data are a reaction to the debate in Germany about the conditions for the supply of weapons to Turkey. Therefore, we do not take this information seriously,” said German Foreign Ministry spokesman Martin Schaeffer, commenting on the deal between Moscow and Ankara about.
In turn, influential Democratic Senator Ben Cardin proposed introducing sanctions against Turkey and thinking about the advisability of its further participation in NATO. As Cardin noted in a letter to the US Treasury Secretary and Secretary of State, the law adopted last month provides for the imposition of sanctions against anyone who carries out major transactions with the defense and intelligence sectors of the Russian Federation.
Earlier, President Recep Tayyip Erdogan announced that Ankara had made the first payment for the S-400 air defense system. In response, the United States expressed its dissatisfaction. In particular, Pentagon spokesman Johnny Miles expressed "concerns" and the "importance of maintaining interoperability within NATO when implementing large military acquisition programs."
He also noted that Turkey is interested in anti-missile systems being developed by NATO allies, including the United States. And he repeated Washington’s position that the weapons of countries outside the alliance, in particular Russia, cannot be combined with those of NATO.
Erdogan reacted extremely harshly. Speaking to the mayors of Turkish cities in Ankara, he said that his country will continue to independently take measures to ensure its security. “They started screaming when we agreed to buy the S-400. What, should we wait for you? We are taking measures on our own and will continue to take them. We ourselves are the masters of our own house,” RIA Novosti reports his words.
And indeed. Türkiye has been conducting unsuccessful negotiations with the United States for several years on the supply of Patriot air defense systems. The country has a 1,300-kilometer border with Syria and Iraq, where there is active fighting, and a chronically hostile Iran, and the Syrians have already shot down a Turkish fighter once.
In addition, Ankara's eternal conflict with its western neighbor and another NATO member - Greece - has long been reduced to. Both sides regularly. But Turkey does not have modern anti-aircraft weapons that it could use against the Greeks, since all NATO systems - both aircraft and air defense systems - are equipped with "friend or foe" identification. Roughly speaking,
a Turkish anti-aircraft missile made in the USA or Germany will simply not fly towards a Greek fighter, since it considers it “one of its own”.
At the same time, Greece had previously acquired Russian air defense systems, which gave it an advantage over Turkish aviation in the Aegean Sea. And, by the way, it became the first NATO member country to actively purchase Russian weapons. So the accusations against Ankara of “violating NATO’s corporate spirit” are not very correct, but the absence of the NATO “friend or foe” system on the export version of the Russian S-400 is one of the main arguments of the United States and Germany.
You need to understand that all export versions of modern Russian weapons have differences (sometimes significant) from the basic configuration supplied to the RF Armed Forces. We are not talking about “climate” adaptations (for example, tanks improved for desert conditions when sold to the Middle East or for humid areas when sold to India). Export options, as a rule, are excluded and have underestimated tactical and technical characteristics.
In addition to the “friend or foe” identification system, the export configuration of the S-400 may not include the 91N6E radar and 48N6M missiles, which will significantly reduce the performance characteristics, but still remains fully responsive to Turkey’s needs, say, for combating aerodynamic targets (cruise or ballistic missile attack on Ankara not a threat). In addition, changes are made to software, which makes it impossible to hack and copy it.
Most hardware experts believe that even if the Turks disassemble each missile and radar piece by piece, they are not able to assemble a similar one on their own without “extra parts remaining,” they are not able to do so.
Lengthy negotiations on the supply of American Patriots broke down because the Turks wanted not only ready-made systems, but also the opportunity to independently produce them on their territory. Turkey does not want to be critically dependent on imports in the military sphere, but the country’s industrial and scientific capabilities do not yet allow them to create something truly modern. The Americans refused to transfer technology, which led to the crisis.
An additional background was the Americans' refusal to hand over the Kurds and the preacher accused in Turkey of organizing a military coup.
In the case of the Russian S-400, the agreement involves not only the supply of two divisions, but also the assembly of two more already in Turkey. On at the moment Ankara does not have the industrial base for the production of such weapons, therefore, the agreement will entail the re-equipment of Turkish production sites by Russian specialists and companies. That is, if we approach this issue formally, Russia will gain access to defense industry and the infrastructure of one of the NATO countries. Together with the construction, this causes a very nervous reaction in Brussels.
Previously, the Turks tried to hastily strengthen their air defense with the help of the Chinese CPMIEC system, which, by the way, is much cheaper than the Russian one. Even then, Ankara was hit with a barrage of accusations from the United States and Europe. They are based on the suspicion that the Chinese will thus penetrate NATO's air defense infrastructure. But this is a clear exaggeration, since the Turkish air defense system is not fully integrated into the overall NATO air defense and there is a tendency for Ankara to withdraw from the overall defensive scheme.
Erdogan refused to purchase Chinese air defense systems, which was presented in Washington and Brussels as a victory. In reality, the refusal of the deal was caused by dissatisfaction with the quality of Chinese air defense systems and the pointlessness of independently copying third-rate products.
The urgent need to cover their borders with air defense means has not gone away, and the Turks naturally turned to the military alliance they belong to, NATO, for help. In 2013, the same “Patriots”, mostly belonging to Germany, were deployed in the south of Anatolia. But subsequently a diplomatic conflict arose between Ankara and Berlin.
The German Constitution limits the German military presence abroad and obliges the Bundestag to regularly conduct inspections of military units outside the country. But Ankara, for ideological reasons, refused to allow German parliamentarians and military personnel to enter its territory for regular inspections. Word for word, conflict, and the German Patriot division left Turkey, since the conditions of its stay violated German laws. Since then, the Germans have harbored a grudge and have become one of the main critics (both officially and through the media) of Ankara’s purchases of non-NATO weapons.
Germany itself does not produce anything similar to the S-400, and therefore cannot be a competitor to Russian weapons. But Berlin took on the role of spokesman for NATO's general opinion about Ankara's “wrong” behavior.
Nevertheless, we can confidently believe that there will not be a fundamental break between Turkey and NATO over the supply of the S-400. For some time we will be watching a fascinating skirmish with mutual accusations. The United States and Germany will talk about “the penetration of Russian technology into the NATO system,” and Ankara will respond with phrases about “the selfishness of Europe” and the “dismissive and commanding tone” with which the NATO leadership talks to the country that has the second largest army in the alliance. But all this “tension” will be virtual. Actually, the NATO Secretary General is already on the purchase of the S-400, but that the purchase of the S-400 is not an alternative to NATO membership for her.
NATO needs Turkey as a “gateway to Asia,” and Turkey needs NATO precisely because of the weakness of the Turkish military-industrial complex, coupled with the urgent need to modernize the huge but... Two S-400 divisions will not be able to reverse this situation.
The newest Russian anti-aircraft missile system (ZRS) S-400 "Triumph" has received permission for export, and negotiations with foreign customers have already begun. Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Federation Dmitry Rogozin and American actor Steven Seagal announced this during the Defense Expo 2014 exhibition, which was visited the day before by Deputy general director air defense concern "Almaz-Antey" Vyacheslav Dzirkaln.
“The system has received an export passport. We are now negotiating the sale of this complex abroad. We have come quite far,” ITAR-TASS quotes Dzirklan. He suggested that a very effective and expensive air defense system is unlikely to be distributed throughout the world.
“Only countries with developed economies and good financial capabilities can afford to purchase such systems,” said the deputy head of the concern, without voicing the cost of Triumph. In 2010, the media reported that the average price of one S-400 complex could exceed $200 million.
"We are now leading marketing activities according to the S-400 air defense system. Yes, the S-300 is an effective complex, but if we already have new developments, why not offer them to our customers and potential partners,” Dzirklan said, noting that “we need to help friends and allies ensure their defense capabilities.”
The S-400 Triumph is a long- and medium-range system that is capable of simultaneously guiding up to 72 missiles at 36 targets at a distance of up to 400 kilometers. The air defense system, designed, in particular, to destroy cruise missiles, tactical and strategic aircraft (including stealth aircraft), as well as ballistic missile warheads, was adopted by government decree of April 28, 2007. The system is capable of detecting a target at a distance of up to 600 kilometers. An important difference between the S-400 and the S-300 are new anti-aircraft missiles with active homing warheads and an increased firing range.
PS According to us, there is nothing sensational in this message. Back in 2009, after two years of trial operation, there were proposals for export deliveries of the S400, the position of the developer of the S400 and subsequent projects Almaz Antey
can be considered critical, most of the leading specialists were fired and employees of the Altair Research Institute were brought into the company, also in an abbreviated version, the company is catastrophically short of funds for normal operation and therefore the decision to sell the C 400 for export can be considered reasonable, so that At least somehow save the development team.
By the way, other enterprises in the industry are in the same situation or worse.
Everything that is happening with the ALMAZ-ANTEY company only confirms the idea that no one in Russia is going to a global confrontation with the EU countries and the USA, there are no means and opportunities for this.
And obviously, without government funding, such industries are doomed to degradation. Well, they will sell a couple of complexes - this will not solve the problems, and competitors may intercept orders.