The determination of a supplier (contractor, performer) begins with the publication of a notice of procurement or, in certain cases, with the sending of an invitation to participate in the determination of a supplier (contractor, performer) and ends with the conclusion of a contract (clause 2 of Article 3 of Law No. 44-FZ). Determining the supplier (contractor, performer) is part of the procurement procedure (clause 3 of Article 3 of Law No. 44-FZ).
Methods for determining suppliers (contractors, performers) are listed in Art. 24 Law No. 44-FZ:
1) competitive methods:
Competition (open, with limited participation, two-stage competition, closed competition, closed with limited participation, closed two-stage competition);
Auction (electronic auction, closed auction);
Request for quotations;
Request for proposals;
2) purchasing from sole supplier.
In accordance with Part 5 of Art. 24 of Law N 44-FZ, the decision on how to determine the supplier (contractor, performer) is made by the customer according to the rules established by this Law. In particular, by virtue of Part 2 of Art. 48 of Law N 44-FZ, the customer must always purchase through an open tender, except for the cases provided for in Art. Art. 56, 57, 59, 72, 83, 84, 93 of Law No. 44-FZ.
Open competition. An open tender is a competitive method of determining a supplier (contractor, performer), in which the customer communicates information about the procurement to an unlimited number of persons by placing a notice of such a tender and tender documentation in the Unified Information System; procurement participants are presented with uniform requirements(Part 1 of Article 48 of Law No. 44-FZ). The deadline for signing the contract by the winner of the competition is 10 days from the date of posting in the Unified Information System the protocol for the consideration and evaluation of applications for participation in the competition. During this period, the winner of the competition must sign a draft contract and submit it to the customer.
Limited participation and two-stage competition. A competition with limited participation is a competitive way to determine a supplier (contractor, performer) who meets the following conditions:
The winner is determined from among the procurement participants who have passed the prequalification selection (Part 1, Article 56 of Law No. 44-FZ). A competition with limited participation is applied in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 56 of Law No. 44-FZ in cases related to the procurement participant having certain qualifications for the supply of goods, performance of work, or provision of services.
A two-stage competition is a competitive way to determine a supplier (contractor, performer), who is subject to the following requirements:
Information about the procurement is communicated by the customer to an unlimited number of persons by posting a notice of such a tender and tender documentation in the Unified Information System;
Procurement participants are subject to uniform requirements or uniform and additional requirements;
The winner is the participant who took part in both stages of the competition and passed the pre-qualification selection at the first stage, if established additional requirements and suggested best conditions execution of the contract (Part 1, Article 57 of Law No. 44-FZ).
Electronic auction. An electronic auction is a competitive way to determine a supplier (contractor, performer), during which the following requirements must be met:
Information about the procurement is communicated by the customer to an indefinite number of persons by posting a notice of the auction and documentation about it in the Unified Information System;
Procurement participants are subject to uniform requirements and additional requirements;
The auction is carried out on an electronic platform by its operator (Part 1, Article 59 of Law No. 44-FZ).
When conducting electronic auction All necessary conditions and requirements related to the supply of goods, performance of work or provision of services are indicated by the customer in the auction documentation (the content of the documentation is specified in Article 64 of Law No. 44-FZ). The draft contract, which is proposed to be concluded based on the results of the auction, is attached to this documentation and forms an integral part of it (Part 4 of Article 64 of Law No. 44-FZ). The deadline for signing the contract by the auction winner was previously established in the auction documentation, but could not be less than 10 days from the date of posting the auction protocol on the official website (for the case provided for in Part 3 of Article 40 of Law No. 94-FZ - 7 days). During this period, the winner had to sign a draft contract and present it to the customer. The deadline for the customer to sign the contract was not determined by law. This gap has been eliminated in the new Law No. 44-FZ.
Request for quotes. A request for quotations is a competitive method of identifying a supplier (contractor, performer), in which information about goods, works or services purchased to meet state or municipal needs is communicated to an unlimited number of persons by posting a notice of a request for quotations in the Unified Information System; The winner is the participant who offered the lowest contract price (Part 1, Article 72 of Law No. 44-FZ).
Detailed information about all conditions for the supply of goods, performance of work or provision of services required by the customer is indicated in the notice of request for quotation (Part 1, Article 73 of Law No. 44-FZ). A draft contract must be attached to such a notice (Part 2, Article 73 of Law No. 44-FZ). The deadline for signing the contract by the winner of the request for quotation is established by the customer in the notice (clause 4, part 1, article 73 of Law No. 44-FZ). If the signed contract is not submitted by the winner within this period, he is considered to have evaded concluding the contract.
Request for proposals. A request for proposals is a competitive way of identifying a supplier (contractor, performer), in which information about a product, work, service purchased to meet state or municipal needs is communicated to an unlimited number of persons by posting a notice of a request for proposals and documentation in the Unified Information System. The winner is the participant who submitted the final proposal that best matches established by the customer requirements for a product, work or service (Part 1, Article 83 of Law No. 44-FZ). Cases in which the customer has the right to purchase through a request for proposals are established by Part 2 of Art. 83 Law No. 44-FZ. All necessary conditions and requirements related to the supply of goods, performance of work or provision of services are indicated by the customer in the notice and in the documentation on the request for proposals (Parts 4, 6, Article 83 of Law No. 44-FZ). The documentation must be accompanied by a draft contract (Part 7, Article 83 of Law No. 44-FZ).
1. Determining the supplier through electronic auctions
Electronic auction- this is a procurement method in which information about the purchase is received from the customer to a selected group of persons through the publication of information about the implementation of this type of purchase and the relevant documentation for it.
When choosing this form of procurement, participants may be subject to general and additional rules, which are provided for when participating on the electronic platform on the basis of the Federal Law dated December 28, 2013 under number 396 Federal Law.
During the procedure holding an electronic auction Participation fees can only be collected from the participant with whom the ETP operator has entered into a procurement contract.
To make it possible take part in an electronic auction To do this, the participant must have registration on a certain ETP. If the participant does not have it, we provide it. To obtain registration, the participant will need to fill out and submit an application, as well as attach a list of documents to it, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 61 44 of the Federal Law.
After this, the site operator issues accreditation to the ETP within 5 days or refuse to receive it, but indicate the reason for the refusal. The participant receives registration on the ETP and its period is 3 years.
If the auction participant provides software for participation in an electronic auction, then he can take part in all auctions that are planned to be held at the specified site.
One of the most important tasks for an ETP operator is maintaining a register of participants in an electronic auction. In this regard, the customer is required to publish a notice in the Unified Information System that an electronic auction has been held. Detailed step by step instructions conducting an electronic auction is described
Do you want to win electronic auctions and enter into profitable contracts?
Contact our “Center”, we will help you win in an electronic auction!
3. Justification for determining the supplier of the electronic auction
When the procurement justification procedure came into effect, mandatory forms were approved for the formation and execution of the procurement plan and schedule.
In the form accompanying the schedule, the customer can include information about the method of selecting a supplier and justify on the basis of what reasons these decisions were made.
Justification for determining the supplier Article 18 of the Law on contract system according to 44 Federal Laws. Its essence lies in justifying the choice of a particular procedure; it is also necessary that this decision be in accordance with the law.
There are special bodies that audit and control the performance of this function. With the correct choice of method for carrying out the procedure, the determination of the contractor is justified.
The main parameters on the basis of which the type of purchase is selected:
- subject of the contract and its terms;
- the criteria by which the winner is selected;
- optimal timing.
WAYS TO DETERMINE SUPPLIERS (CONTRACTORS, PERFORMERS) IN THE CONTRACT SYSTEM
In contrast to Law No. 94-FZ, which divided all methods of placing an order into unconditionally permitted tenders and others (non-tenders), which could only be used under certain, stipulated conditions, in Law No. 44-FZ methods are divided into competitive and procurement from a single supplier (contractor, performer) (hereinafter referred to as supplier) (Fig. 3.5).
Despite international experience in procurement activities and the opinion of the Russian expert community, the very text of the basic law contained a mechanism that would not allow competition to become a priority method of procurement in Russian Federation. On the one hand, according to Part 2 of Art. 48 of Law No. 44-FZ, in all cases, the customer carries out procurement through an open tender, with the exception of situations provided for by this law of limited use of other procurement methods 1. On the other hand, the cases of using an electronic auction were not clearly limited, which should have been carried out by the customer in the event that the procurement object was included in the lists established by the Government of the Russian Federation and, possibly (in the presence of regulatory acts of the subjects), executive bodies state power subjects of the Federation. In accordance with Part 3 of Art. 59 of Law No. 44-FZ, the customer received the right, through an electronic auction, to purchase goods, works, and services not included in the above lists. After this, de jure the competition ceases to be the only priority method. If we take into account the exhaustive list of products approved by Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2013 No. 2019-r (now no longer in force), it becomes obvious that the main method of procurement is no longer a competition, but an electronic auction. As a basic performance criterion
Rice. 3.5.
this means ensuring maximum savings budget funds and, quite naturally, to the detriment of the quality of the purchased products.
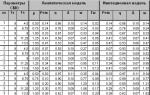
The choice of alternative procurement methods, as in Law No. 94-FZ, was determined primarily using a restrictive price criterion (Table 3.1)